How Blockchain works-
I'm going to try to tackle the whole blockchain technology
thing and we're going to understand how it looks down to the tiniest
detail. I'll be as simple as possible when explaining but I will also
tackle some of the mathematical parts of the technology so let's
start .
1. Blockchain Definition
2. Centralized Architecture
3. Decentralized Architecture
4. Distributed Architecture
5. Ledger
Systems
6. Hashing
7. Proof of Work
8. Mining
Blockchain Definition-
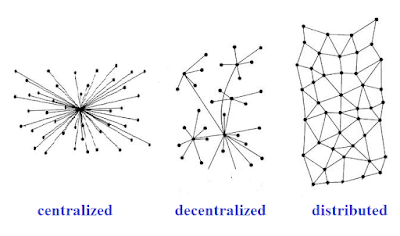
So blockchain is a decentralized distributed public Ledger's system now let's break down the definition and understand every technical jargon the first few technical terms that we encounter are decentralized and distributed to understand what it means to be decentralized and distributed let's start with the status quo.
Centralized Architecture-
Now the centralization is like any organization of network where decisions regarding the organizations are made by a chosen group of people in the centralized system. Presently we are surrounded by a massive centralized system which we use every day be if you want to order food from some delivery and logistics system like Zomato or you want to book a cab through any taxi service app like uber or ola you're getting service third party.
This third party has complete authority on the rules and regulations of the system even though these guys have a majority of the power they greatly depend on your charge to stay functional for example I'm sure you keep your money in the banks instead of just doing it away under your bed or locker at home because we trust bank more than your next-door neighbour.
Decentralized Architecture-
A decentralized system is the opposite of a centralized system. When any service is ruled by no single governing authority then those system are called decentralized system for example internet. Nobody owns the internet and nobody is supervising what websites and networks we are going through.
Distributed Architecture-
But what does it mean to be distributed so do you understand what a distributed system is let's look back and analyze what has been the common reason for a majority of the data breaches of the past. So in 2013 mega-giant, Yahoo faced a massive data breach which impacted around 3 billion users than in 2014.
eBay faced a cyber attack that compromised the user data for our 145 million profiles again in 2016. One more website Adult Friend Finder was also attacked hackers collected around 20 years of data on six databases that impure names, email ,addresses and passwords.
All these attacks were successful because these companies chose to keep all their data in one basket or if I may say one server which makes it very easy for a hacker to creep in and do creepy stuff by distributing everything everywhere the hacker would need to change the data in all the places at once blockchain is distributed and decentralized.
This means that whatever is stored on a blockchain is distributed and the blockchain in itself is owned by no single governing body by distributing everything everywhere a bad actor would need to change the data in all places at once in order to do their sneaky things it feels weird but by opening up and giving the data to everyone you protect it. So what we see from breaking down the definition so far is that blockchain is a system which is owned by nobody and instead is distributed in nature.
Ledger Systems-
Now would like to tell you the other half of the definition which states that blockchain is a public ledger system .So first of all let's get our heads around this whole ledger system a ledger is a list of anything the term ledger originates from banking as it was first going to denote a list or a book containing financial transactions now about blockchain technology what exactly is a ledger well it's all the transactions that are committed on the network to understand what I mean let's jump back to the genesis of blockchain technology.
So the birth of blockchain technology date sparked in 2009 and the timing was impeccable while the world was facing one of the toughest economic crisis a group or person under the pseudonym of Satoshi Nakamoto introduced to the public Bitcoin a digital currency not owned by the government but in essence very much like fiat currency or some of you would call cash so in the sense it could be spent anonymously it could be hard to track and it is easily trusted now the underlying tech that powered Bitcoin was blockchain. So any transaction that was made using Bitcoin as a currency was registered on a list called and this Ledger was then distributed to all the members that had agreed to participate in the network everybody could essentially keep tabs on each other's transactions and to anybody trying to tamper with records would be easily identified due to the distributed nature of the system
Now since the meteoric increase in both value and fame of Bitcoin other such networks have come up with each Network ranked decentralized some service or the other but the fundamentals of the network remain the same. So now that I've explained what it means to be a job let's try and understand what it means to be public so it is hard to fathom the power of public when it comes to blockchain because it's the participants or the public whatever I call him is responsible for the most integral part of the system that is validation.
So let's take a scenario where a blockchain network has only four participants namely a B C and D every time one of them spent some money in Bitcoin. They broadcast the transaction down to the last detail onto the network but how are the remaining members supposed to know what a is saying indeed is valid or not this is handled by block chains unique method of validation called consensus.
This means that every participating member must agree or come to consensus regarding the validity of the transaction every network has its own unique way of achieving consensus and bitcoin protocol uses a method called proof of work.
The article is going to get a little more tactical as we are going to be discussing a few new technical jargons from here on but I'll try my best to be as simplistic as possible now let's go back to the little scenario. I had just discussed and here a broadcasts a transaction to the rest of the network now let's also assume that this is not the first transaction of the network and this particular transaction is an addition to an already ongoing list of transactions that have already been piloted every time a new transaction is committed to the network a new block gets created and all these transactions are firstly hashed.
Hashing-
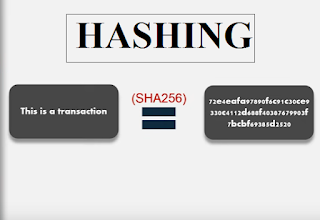
So what exactly is hashing to answer simply hashing is a process of converting a long string into a unique string generally of much shorter and fixed length what is important to understand for you as a viewer is that the generated hash depends completely on the input even a slight change in the input will change the output hash completely.
Secondly in blockchain a unique kind of hashing is used and this is called cryptography caching because they cannot be practically reverse engineered. So now to get a better understanding of hashing and how it integrates into blockchain. Let's think back I had just mentioned that the list of transaction is taken together and hashed so the output hash or the digest is called the block hash and stands as a unique identifier of that certain block so suppose he were to sneakily try and change the history of transactions in a certain block the output block hash would be changed drastically which would easily denote that something has been tampered with.
So right now our focus is to see how a function can prove that a particular list of transaction is truthful imagine someone shows you a list of transactions and they say hey I found a special number so that when you put that number at the end of this list of transactions and apply sha-256 to the entire thing the first 30 bits of that output are all zeros how tough do you think it would be to figure out that number.
|
So let's bring in some math here let's say the harsh is only made up of ones and zeroes and it's 256 characters long in such a case the probability that a harsh happens to start with thirty successive zeroes is around 1/2 raised to 30 which is about one in a billion and because sha-256 is a cryptographic hash function the only way to find the special number is just guessing and checking so the person trying to check validity of the block almost certainly had to go through about a billion different numbers before finding the special one and once you know number it's really quick to verify you just run the hash and see that there are thirty zeros in other words you can verify that they went through a large amount of work but without having to go through the same effort yourself this is called proof of work.
What's important is that all of this work is intrinsically tied to the list of transactions if you change one of those transactions even slightly it would completely change the hash so you'd have to go through another billion guesses find new proof of work or a new number that would start 30 zeros when tied up with the altered list nothing back to our distributed ledger situation where everyone is there broadcasting their transactions and we want to wait for them to agree on what block is correct as I said the core idea behind the original Bitcoin people is to have everyone trust whichever ledger has the most work put into it the way this works is to first organize a given ledger into blocks now in the same way a transaction is only considered valid when it's signed by the sender a block is only considered valid if it has a proof of hope.
Proof of work-
So, how proof of work is actually helping us in identifying any sort of mismatch in a transaction so firstly now imagine there's this list of five transactions between a B, C and D and the block hash is whatever you see in the diagram.
Now if you were to slightly change any transaction or if you were to slightly change the order of the transaction the complete hash is changed drastically so this will easily tell anybody that the proof of work is wrong as he can compare it with the other block genes on are the copies and this is how you reach consensus that this block is not valid.
So that explains how proof of work ties in with blockchain now also to make sure that there's a standard order to these blocks we'll make it so that a block has to contain the hash of the previous block as its header.
So firstly it already contains the transaction and the proof of work which looks something like this and now the next block will also have the block hash of the previous block. So it'll look something like this now since the block hash has been chained we can see a certain chain being formed so instead of just calling it sledge the system is being commonly known as a blockchain .
So the last part that's left is mindless now every time someone validates a certain block after putting it in all the work to find a special number the system rewards them but since Network-specific cryptocurrency. Now in the Bitcoin protocol currently the block reward as February 2, 2018 is 12.5 bitcoins not only does is incentivize system the network running but also generating currency.
Now some people have invested in high-performance GPUs. So that they can validate new blocks quicker than the others and earn and live off the block rewards these people are known as miner. So friends I think I've covered most aspects of blockchain.
We understood how blockchain is a decentralized and distributed system we saw the public nature of blockchain and how influence he ties up the public participation using incentivization. we also read about how the security and integrity of the system is maintained using cryptography hash functions tied up with a consensus mechanism and this brings us to the end of the article I hope you enjoyed and learn something new from my article .










![Download free pc games[websites]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/a/AVvXsEiVaGKI6OZhn8AJwIaM1mqML8WGH7WmiwUtHlnJs24316gAQi5hsaazOcaTuSBxg4X-CVEpEuvLtlNdJSydAqzlj4N7LEh3Ti_xMujC3jV8vd2mEklpSQIgvgrMW_WykIIF1NLrPWn40b4Xj9tVj-LQjvc-HJlXUeGcI6YlE92a0isLHy2NMhVF468i=w100)




0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.